Key Takeaways
- Achilles tendonitis is common but highly treatable, especially with early intervention.
- Recognizing symptoms early, reducing activity, and initiating treatment can prevent chronic issues.
- Effective management includes rest, physical therapy, supportive footwear, and sometimes medication.
- Prevention focuses on gradual activity changes, proper footwear, and regular stretching.
- Persistent symptoms warrant consultation with a podiatrist or other healthcare professional.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Achilles Tendonitis
- Recognizing the Symptoms
- Effective Treatment Strategies
- Preventive Measures
- When to Seek Professional Help
- Final Thoughts
Understanding Achilles Tendonitis
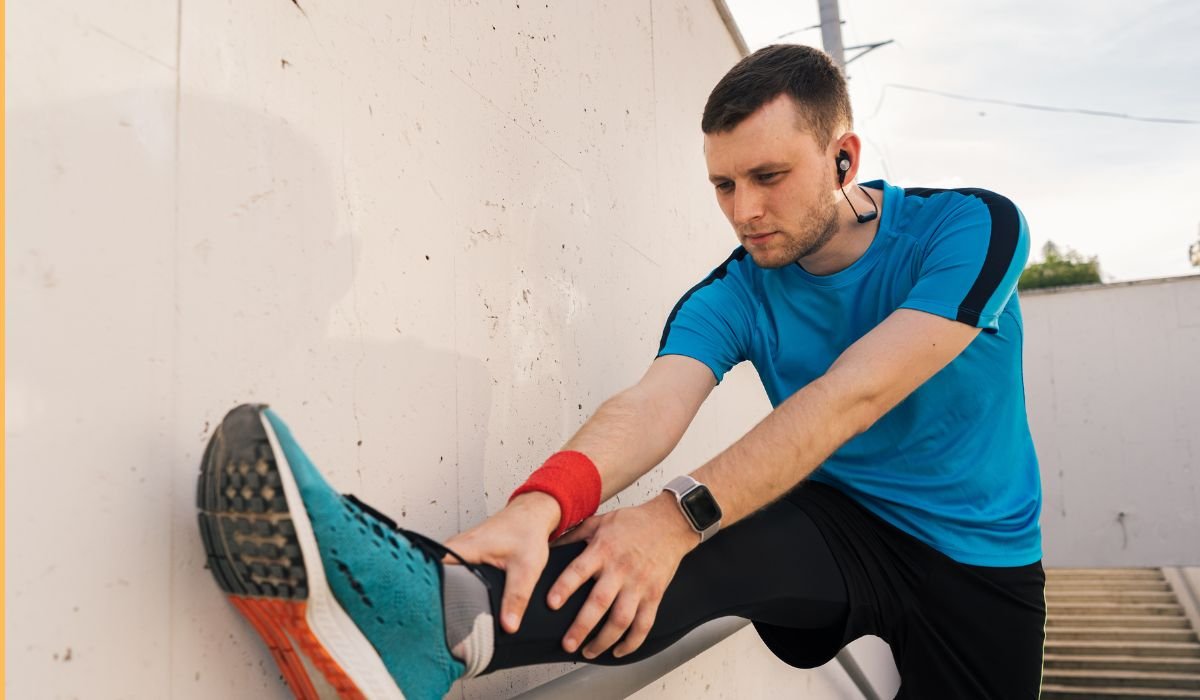
Achilles tendonitis is a common overuse injury that affects the tendon connecting the calf muscles to the heel bone. It often develops from repetitive stress, particularly in athletes or individuals who suddenly increase the intensity of their physical activity. Symptoms typically include pain, stiffness, and swelling around the back of the heel, which may worsen after exercise or first thing in the morning. Left untreated, the condition can progress to more serious complications, such as chronic pain or even tendon rupture, making early recognition and proper management essential.
When dealing with persistent discomfort, individuals often seek professional guidance to determine the most effective course of treatment. Consulting a specialist, such as a podiatrist Northampton PA, can provide valuable insights into preventive measures and recovery strategies. Management may involve rest, stretching exercises, supportive footwear, and physical therapy. Addressing the condition early helps maintain mobility, prevent worsening injury, and support long-term foot health.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of Achilles tendonitis is key to preventing further complications. The most common sign is pain along the back of the leg or just above the heel, often worse in the morning or after physical activity. Swelling and tenderness in the area can also occur, making walking, running, or climbing stairs uncomfortable. Stiffness in the tendon, especially after rest periods, is another frequent symptom. In some cases, a thickened tendon or creaking sensation may be felt. Identifying these warning signs early allows for timely care and reduces the risk of long-term damage.
Effective Treatment Strategies
The foundation of Achilles tendonitis management centers on reducing stress to the injured tissue, allowing it to recover and regenerate. Conservative care—when initiated early—is highly successful for most patients.
- Rest and Activity Modification: Temporarily step back from running, high-impact sports, or any activities that exacerbate symptoms. Substitute with low-impact exercises, such as swimming or cycling, when appropriate.
- Physical Therapy: Targeted exercises prescribed by a physical therapist can stretch and strengthen the calf muscles, relieving strain on the Achilles. Eccentric loading exercises are particularly effective in both pain relief and tendon healing.
- Medications: Over-the-counter NSAIDs (such as ibuprofen) reduce swelling and pain, providing symptomatic relief.
- Orthotics and Heel Lifts: Orthotic devices and shoe inserts can cushion the heel and lessen tensile forces on the tendon. They are especially important if gait abnormalities or flat feet are present.
- Cold Compresses and Support: Icing the affected area and wearing supportive footwear or braces may decrease inflammation and provide stabilization.
In more severe or persistent cases, your medical provider may suggest additional therapies, such as shockwave treatment, corticosteroid injections (with caution), or, in very rare instances, surgical intervention for tendon repair.
Preventive Measures
Prevention is more effective—and less disruptive—than managing chronic symptoms. Protect your Achilles tendon by:
- Increasing activity intensity and duration gradually, never making sudden leaps in workout demands
- Incorporating regular calf stretches and strength exercises into your fitness routine
- Choosing supportive, well-fitted shoes that cushion the heel and provide arch support
- Warming up thoroughly before strenuous exercise and cooling down afterward
- Listening to pain signals and resting as needed, rather than “pushing through” discomfort
Lifestyle adjustments—such as cross-training, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding repeated hard-surface activities—can also help mitigate risk over time. Prevention becomes easier when you view everything as part of a long-term recovery and fitness strategy.
When to Seek Professional Help
If self-care measures do not resolve your symptoms within two weeks, or if pain intensifies, consult a healthcare professional promptly. Significant swelling, sudden loss of function, severe pain, or an audible “pop” may indicate a more serious injury that requires urgent medical attention, including potential tendon rupture.
Consulting a podiatrist or sports medicine provider ensures you receive a thorough evaluation, diagnostic imaging if needed, and a tailored treatment protocol. Early guidance not only speeds recovery but also decreases your chances of recurrence.
Final Thoughts
Achilles tendonitis, while common, can be effectively managed with early care and preventive strategies. Recognizing symptoms promptly, making lifestyle adjustments, and seeking professional help are key to protecting long-term tendon health and mobility.
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE: The Top 6 Signs You Need Pest Control Immediately