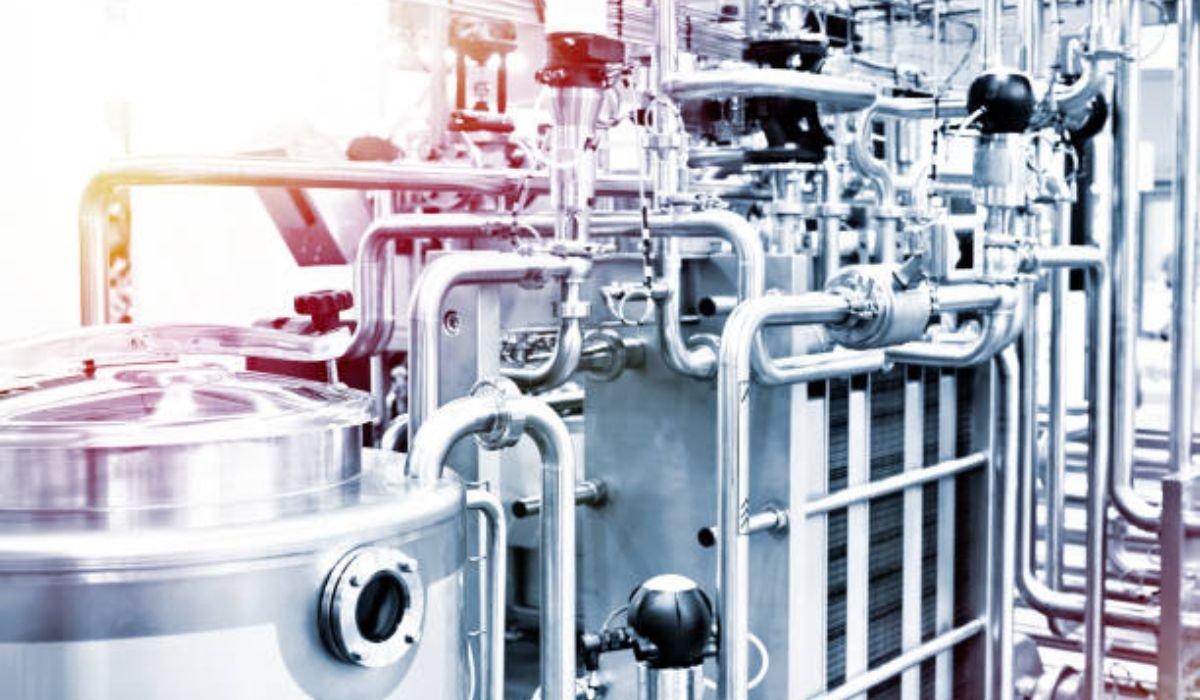
Heat exchangers form the backbone of thermal management in critical industrial environments, enabling operations ranging from power generation to chemical processing and HVAC systems. With industries demanding ever-increasing efficiency, durability, and adaptability, next-generation solutions—such as advanced thermocouple connectors—have become crucial to upgrading legacy systems and integrating state-of-the-art monitoring and performance capabilities.
Across the globe, engineers are not only developing new heat exchanger technologies but are also reimagining their design, operation, and role in driving industrial sustainability. Through a synergy of smart digital tools, innovative materials, and hybrid systems, the heat exchanger landscape is being redefined to deliver unmatched energy recovery, predictive maintenance, and space-saving capabilities—helping entire sectors adapt to modern challenges.
Additive Manufacturing Revolutionizes Design
Additive manufacturing, more commonly known as 3D printing, has revolutionized the possibilities in heat exchanger design. By fabricating highly complex and customized internal channel geometries, these methods facilitate optimal heat transfer while reducing pressure drops—crucial metrics for industries that rely on compact, efficient heat exchange. Researchers at the University of Wisconsin-Madison reported an impressive 27% uplift in power density over traditionally manufactured counterparts, thanks to their ability to create intricate, twisting channels that conventional processes cannot machine. Such breakthroughs are particularly transformative for aviation and space applications, where weight and space savings have a significant impact on system performance.
Smart Monitoring and Predictive Maintenance
Sensors, IoT devices, and networked control systems are quickly becoming standard in new heat exchanger installations. By collecting real-time data on flows, temperatures, pressures, and vibrations, these advanced monitoring systems enable dynamic adjustments and the immediate identification of anomalies. The integration of artificial intelligence enables predictive maintenance, providing early warnings about fouling, corrosion, or potential leaks, allowing operators to perform targeted interventions before costly failures occur. The result is higher uptime, substantial cost savings, and a reduced environmental footprint through optimized energy use.
Advanced Materials Enhance Efficiency
Advanced material science continues to enhance the durability and effectiveness of heat exchangers. The adoption of exotic alloys—such as titanium, Inconel, and duplex stainless steels—along with novel composites, results in greater heat transfer efficiency and exceptional resistance to corrosion and thermal fatigue. These materials perform reliably even in the harshest environments, such as offshore oil rigs, chemical processing plants, and nuclear power stations. Modern coatings and surface treatments not only prolong equipment life but also ensure stable performance. Key research highlights include enhanced fouling resistance coatings and self-cleaning surfaces that reduce maintenance intervals and optimize heat exchange.
Hybrid Systems for Optimized Performance
Hybrid heat exchanger designs are increasingly favored for their ability to maximize energy transfer within the smallest possible footprint. By combining plate-fin with shell-and-tube or spiral-wound mechanisms, hybrid systems cater to the demanding operational requirements of applications such as liquefied natural gas (LNG) production, large-scale chemical manufacturing, and advanced water desalination facilities. These designs offer the best attributes of their component types—blending the compact, easy-to-clean benefits of plate systems with the robust, pressure-resistant features of tubular exchangers.
Sustainability and Energy Recovery
With carbon regulations intensifying and public demand rising for greener operations, industrial heat exchanger manufacturers are shifting to sustainable options that prioritize energy recycling and minimize resource waste. Sophisticated designs now tap into waste heat streams for secondary use. In contrast, the integration of heat exchangers in geothermal plants and solar thermal power has become common, as indicated by a 16% annual increase in deployment. These measures not only reduce greenhouse gas emissions but also yield significant energy savings across the board.
Digital Twins and AI Integration
Digital twins are reshaping the management and analysis of heat exchanger systems. With a digital twin, facility managers maintain a real-time, virtual replica that mirrors every operational aspect of the physical plant. Combined with artificial intelligence, these tools automatically optimize performance parameters, forecast maintenance needs, and create autonomous control loops that minimize the need for manual intervention. The potential for system learning and adaptation driven by live operational data makes this one of the most disruptive trends in large-scale industrial installations.
Compact Designs for Space Efficiency
The modern urban environment and retrofitted industrial sites often present significant spatial constraints. Compact heat exchanger formats, specifically modular plate heat exchangers, dominate new builds and upgrades. Offering ease of expansion, unmatched thermal transfer per footprint, and simplified servicing, these solutions allow architects and engineers to optimize HVAC systems for both ultra-high-rise buildings and delicate laboratory environments without sacrificing performance. Their versatility also allows for rapid adaptation to changing duty requirements in multi-purpose facilities.
Conclusion
Innovations in heat exchanger technology are rapidly reshaping the possibilities for efficient heat management across every industrial sector. Through the convergence of smarter monitoring, resilient materials, hybrid and compact designs, and sustainable operations, heat exchangers are not only more efficient but integral to achieving environmental goals and maximizing operational uptime. These ongoing advancements ensure that industries globally remain resilient and ready for the challenges of tomorrow’s energy and climate demands.
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE: Unveiling the Power of Large Ultrasonic Cleaners for Industrial Precision