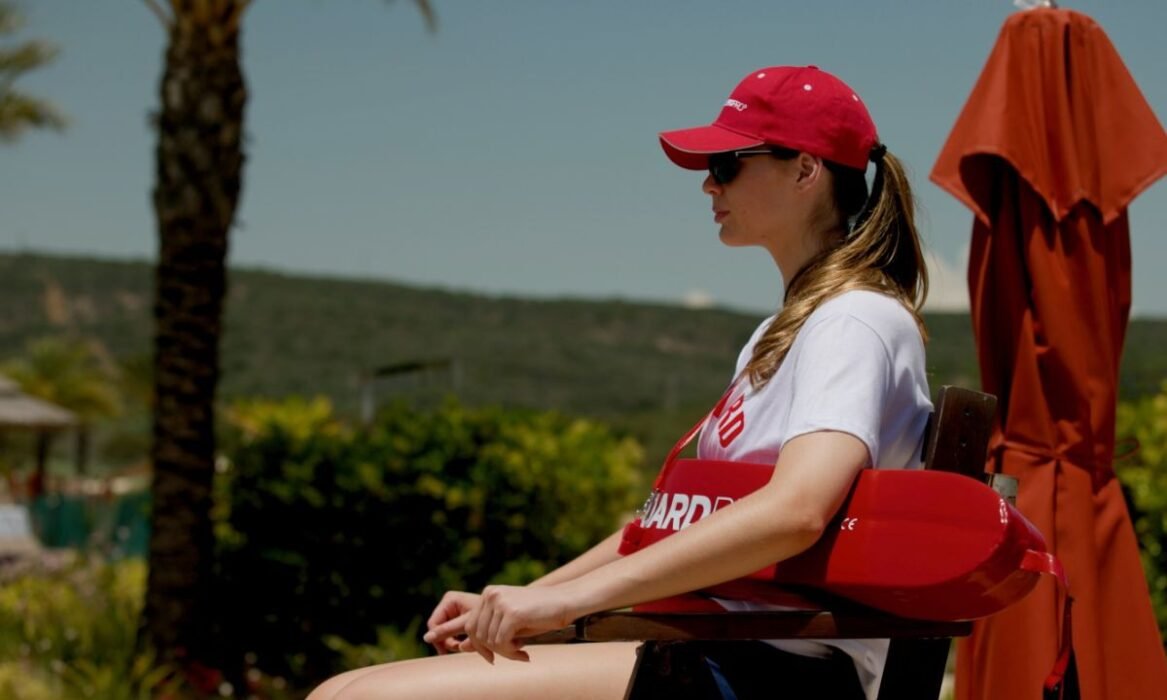
Becoming a professional lifeguard involves acquiring specific credentials that guarantee readiness to deal with emergencies and maintain safety in aquatic environments. Here is a top to bottom exploration of the essential requirements and skills necessary for this indispensable role:
CPR Training: Quick Response to Cardiac Emergencies
CPR training is a foundation of lifeguard certification. It outfits lifeguards with the knowledge and skills expected to perform chest compressions and rescue breaths on individuals experiencing cardiac capture. Prompt CPR can significantly increase the possibilities of endurance until cutting edge clinical assistance shows up, making it an essential skill for any professional lifeguard.
First Aid Skills: Essential for Managing Injuries and Illnesses
Capability in first aid is indispensable for lifeguards responsible for the safety of pool and beachgoers. This training covers many scenarios, including wound care, splinting, and treating normal injuries like cuts, scraped areas, and sprains. Lifeguards should be ready to deal with health related emergencies expeditiously and successfully to minimize intricacies and guarantee the prosperity of those under their consideration.
Water Rescue Techniques: Swift and Safe Extrication
Lifeguards go through thorough training in water rescue techniques to work with safe extrication of individuals in trouble. These techniques include reaching helps, where a lifeguard broadens a rescue cylinder or shaft to a swimmer in inconvenience, and throwing helps, using toss ropes or light gadgets to contact individuals further from shore.
Also, lifeguards are trained in swimming rescues, enabling them to explore fierce waters and bring troubled swimmers to safety.
Physical Fitness Requirements: Stamina and Strength
Physical fitness is a fundamental requirement for lifeguards, who should maintain stamina and strength to successfully play out their obligations. Lifeguard fitness standards frequently include timed swimming tests to survey perseverance and deftness, as well as strength activities to guarantee the capacity to execute rescues and aid emergency situations without weakness.
Knowledge of Aquatic Facilities: Understanding the Environment
Knowledge of the design and operational protocols of aquatic facilities is crucial for lifeguards. This knowledge empowers them to expect possible hazards, uphold safety rules, and answer immediately to emergencies within their appointed region.
Lifeguards should know about specific safety highlights, for example, emergency exits, safety gear areas, and water profundity varieties, to maintain a solid environment for patrons.
Continuous Training and Skill Maintenance: Staying Ready
Professional lifeguards take part in ongoing training to improve their skills and readiness. Continuous education includes customary practice of rescue techniques, refreshes on CPR and first aid guidelines, and support in reenacted emergency scenarios. This training guarantees that lifeguards remain certain and able in their capacity to deal with erratic situations and give compelling assistance when required.
Communication and Leadership Skills: Essential for Successful Response
Compelling communication is basic for lifeguards to pass instructions obviously on to patrons and coordinate with colleagues during emergencies. Lifeguards should have strong interpersonal skills to console upset individuals and direct spectators to aid emergency response endeavors.
Leadership skills are additionally crucial, enabling lifeguards to assume responsibility for challenging situations, focus on activities, and successfully oversee assets to guarantee the safety of everybody in their consideration.
Professionalism and Ethical Obligations
Past specialized skills, professionalism and ethical lead are integral to the role of a lifeguard. Lifeguards are entrusted with the safety and prosperity of swimmers and beachgoers, requiring a commitment to watchfulness and responsiveness consistently.
Professionalism involves maintaining a quiet disposition under tension, adhering to laid out safety protocols, and continuously assessing and mitigating gambles in the aquatic environment. Ethical obligations include treating all individuals with deference and poise, paying little heed to progress in years, foundation, or ability to swim, and promoting inclusivity and accessibility in aquatic diversion. Lifeguards act as role models for water safety, fostering a culture of awareness and readiness among patrons and colleagues the same.
This expansion develops the importance of professionalism and ethical obligations in the role of a lifeguard, emphasizing their basic role past specialized skills in ensuring safety and promoting a positive aquatic environment.
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE: Misty Severi: A Journey Through Journalism and Advocacy
Final Word: Commitment to Safety and Professionalism
In conclusion, the credentials necessary for a professional lifeguard encompass lifeguard certification, CPR training, first aid skills, capability in water rescue techniques, physical fitness, knowledge of aquatic facilities, continuous training, and strong communication and leadership abilities. These qualifications are essential for safeguarding the prosperity of individuals in aquatic environments, from public pools to open water settings.
For aspiring lifeguards, obtaining certification through organizations like the American Lifeguard Association gives complete training and approval of these essential skills, ensuring readiness to answer emergencies and maintain safety with professionalism and dedication.