Malaria remains one of the most challenging infectious diseases globally, responsible for hundreds of thousands of deaths each year. Amidst the ongoing search for effective treatments lies a surprising candidate: Labrador Tea. Traditionally used by the First Nations of Nunavik, Canada, for its medicinal properties, this northern plant has stepped into the scientific spotlight with its potential efficacy against malaria. This blog post delves into the traditional uses of Labrador Tea, the recent scientific discovery, and the promising future implications for malaria treatment.
Fragrant Brew Used In Traditional Medicine
A Cultural Heritage of Healing
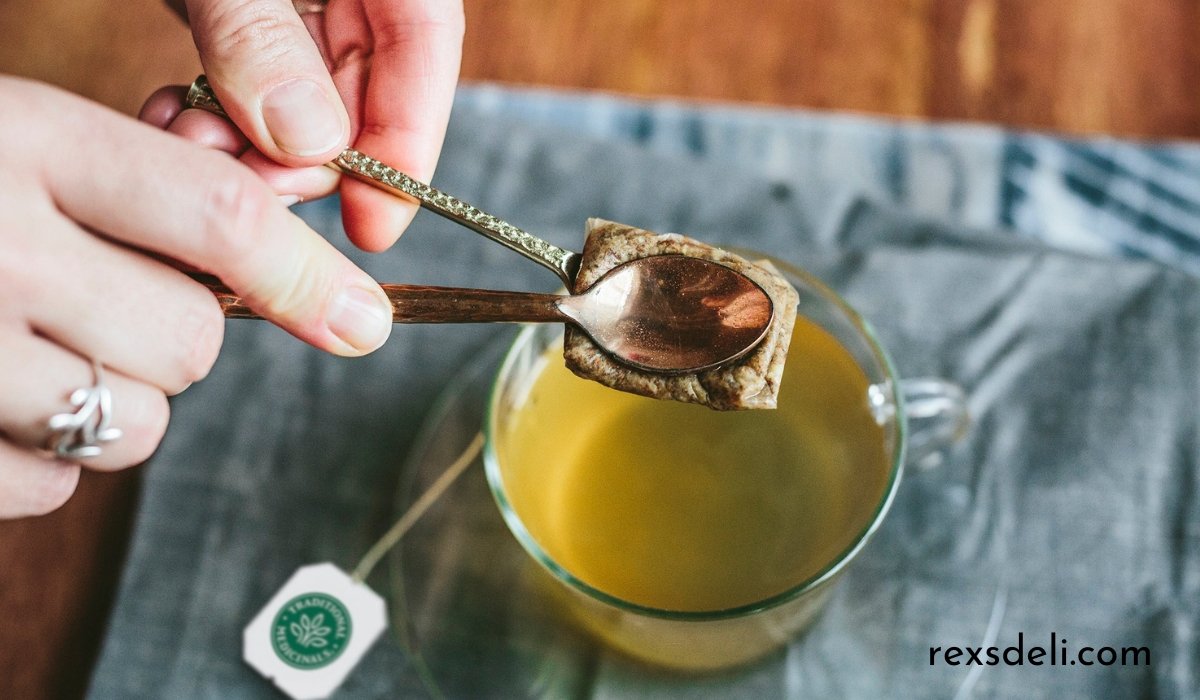
Labrador Tea, known scientifically as Rhododendron groenlandicum, has a rich history embedded in the traditional medicine of the First Nations communities in Nunavik, Canada. For centuries, these indigenous peoples have harnessed the natural properties of Labrador Tea to treat various ailments. The fragrant brew made from its leaves was more than just a comforting drink; it was a cornerstone of their medicinal practices.
The plant’s therapeutic uses include treating ailments such as respiratory conditions, digestive issues, and skin problems. The aromatic leaves were also employed in topical treatments for wounds and insect bites, showcasing the plant’s versatile medicinal properties. This traditional knowledge has been passed down through generations, reflecting a deep understanding of the local flora and its benefits.
A Fragrant Brew Used in Traditional Medicine
The preparation of Labrador Tea involves brewing its dried leaves, resulting in a fragrant tea known for its soothing effects. This “fragrant brew used in traditional medicine” is credited with significant health benefits, including anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. The tea was often consumed to alleviate symptoms of colds, flu, and other respiratory conditions, providing relief through its calming and therapeutic effects.
The First Nations’ use of Labrador Tea highlights the importance of traditional knowledge in identifying and utilizing natural remedies. This historical context sets the stage for contemporary scientific exploration, aiming to validate and potentially expand the medicinal use of this remarkable plant.
Scientific Discovery
Unveiling the Medicinal Secrets
Recent scientific investigations have turned a keen eye on Labrador Tea, revealing its promising potential in malaria treatment. A team of researchers conducted a comprehensive study, identifying bioactive compounds within the plant leaves. Among these compounds, one stood out for its efficacy against Plasmodium falciparum, the parasite responsible for the deadliest form of malaria.
The Compound’s Mechanism of Action
The identified compound, currently under detailed scrutiny, exhibits a unique mechanism of action that disrupts the life cycle of Plasmodium falciparum. Unlike conventional antimalarial drugs, which often target specific stages of the parasite’s development, the compound from Labrador Tea affects multiple stages. This broad-spectrum efficacy could prove crucial in overcoming drug resistance—a significant hurdle in current malaria treatment efforts.
Laboratory tests have shown that this compound effectively inhibits the growth of the malaria parasite, reducing its ability to reproduce and spread. These findings are a testament to the untapped potential of traditional medicinal plants and underscore the importance of integrating indigenous knowledge with modern scientific research.
Future Implications
A New Era in Antimalarial Drug Development
The discovery of an effective antimalarial compound within Labrador Tea opens new avenues for drug development. Researchers are now focused on isolating and synthesizing this compound to create a new class of antimalarial drugs. Given the growing resistance to existing treatments, a novel drug from Labrador Tea could be a game-changer in the global fight against malaria.
The Importance of Studying Traditional Medicinal Practices
This discovery also emphasizes the value of studying traditional medicinal practices. Indigenous knowledge has long been a repository of medical wisdom, often overlooked by modern science. By bridging the gap between traditional knowledge and contemporary research, we can uncover new treatments for various diseases, preserving cultural heritage while advancing medical science.
Potential Challenges and Considerations
While the prospects are promising, several challenges remain. Extensive clinical trials are required to determine the compound’s safety and efficacy in humans. Additionally, ethical considerations must be addressed, ensuring that the First Nations communities benefit from any commercial applications arising from their traditional knowledge.
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE
Ulcuprazol:Determining the Gerd and Sex of an Unborn Child Scientific Perspective
Conclusion
The journey of Labrador Tea from traditional medicine to a potential modern cure for malaria is a compelling narrative of cultural heritage meeting scientific innovation. As we continue to explore and validate the medicinal properties of indigenous plants, we unlock new potentials for treating some of the world’s most persistent diseases.
While the road ahead includes rigorous testing and ethical considerations, the discovery of a compound in Labrador Tea effective against Plasmodium falciparum marks a significant milestone. This fusion of traditional knowledge and scientific inquiry not only offers hope for new malaria treatments but also highlights the critical role of indigenous wisdom in advancing global health.
FAQs
- What are the traditional uses of Labrador Tea?
Labrador Tea has been used by the First Nations communities in Nunavik for treating respiratory conditions, digestive issues, and skin problems, among other ailments.
- What are the health benefits of Labrador Tea?
Labrador Tea is known for its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and soothing properties, making it effective in alleviating symptoms of colds, flu, and respiratory conditions.
- How does the antimalarial compound in Labrador Tea work?
The compound disrupts the life cycle of Plasmodium falciparum, the parasite responsible for malaria, by affecting multiple stages of its development.
- What are the future implications of Labrador Tea in medicine?
The discovery of an antimalarial compound could lead to the development of new drugs and underscores the importance of integrating traditional knowledge with modern science.
- What challenges need to be addressed in developing drugs from Labrador Tea?
Extensive clinical trials and ethical considerations are required to ensure safety, efficacy, and fair benefit-sharing with First Nations communities.