Understanding Turbocharged Diesel Engines
Turbocharged diesel engines have revolutionized transportation and heavy machinery. These powerful systems offer advantages over naturally aspirated engines, providing improved fuel efficiency, increased power output, and reduced emissions. Let’s explore the key components and principles behind these impressive powerplants.
How Turbochargers Work
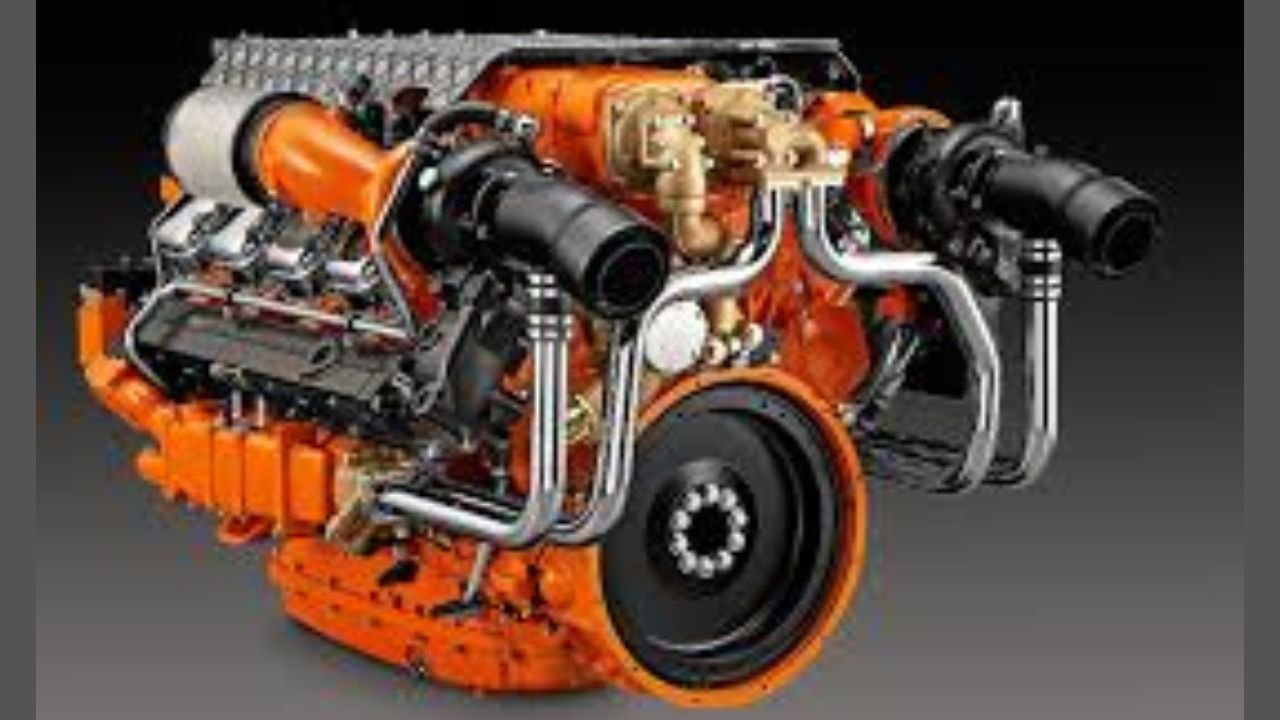
Turbochargers are ingenious devices that harness the energy from exhaust gases to compress incoming air, delivering more oxygen to the combustion chamber. This process allows for more fuel to be burned efficiently, resulting in greater power output. The main components of a turbocharger include:
- Turbine wheel
- Compressor wheel
- Center housing
- Wastegate
The turbine wheel spins as hot exhaust gases pass, driving the compressor wheel via a shared shaft. The compressor wheel draws in and compresses ambient air, forcing it into the engine’s intake system.
Benefits of Turbocharged Diesel Engines
Turbocharged diesel engines offer numerous advantages over their naturally aspirated counterparts:
- Increased Power Output: Turbochargers enable engines to produce significantly more power from a smaller displacement by forcing more air into the combustion chamber.
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: The increased air pressure allows for more complete fuel combustion, leading to better fuel economy.
- Reduced Emissions: More efficient combustion results in cleaner exhaust gases, helping engines meet strict environmental regulations.
- Better Performance at Altitude: Turbochargers can compensate for the thinner air at higher elevations, maintaining engine performance.
- Enhanced Torque: Turbocharged engines typically produce more low-end torque, improving acceleration and towing capabilities.
Common Applications of Turbocharged Diesel Engines
Turbocharged diesel engines are widely used in various applications due to their power and efficiency:
- Heavy-duty trucks and buses
- Construction and mining equipment
- Agricultural machinery
- Marine vessels
- Generators and power plants
- Passenger vehicles
Maintaining Turbocharged Diesel Engines
Proper maintenance is crucial for ensuring the longevity and performance of turbocharged diesel engines. Here are some key maintenance tips:
- Regular Oil Changes: Use high-quality oil and change it according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Air Filter Replacement: Clean or replace air filters regularly to prevent contaminants from entering the engine.
- Cooling System Maintenance: Ensure the system is functioning properly to prevent overheating.
- Fuel System Care: Use clean, high-quality diesel fuel and replace fuel filters as recommended.
- Turbocharger Inspection: Regularly inspect the turbocharger for signs of wear or damage.
Upgrading Turbocharged Diesel Engines
For those seeking even more power and performance, upgrading components of a turbocharged diesel engine can yield impressive results. One popular upgrade is replacing the stock turbocharger with a more efficient model. For example, the Detroit 12.7 turbo is popular for certain engine models, offering improved airflow and boost pressure.
Other common upgrades include:
- High-flow air intake systems
- Larger intercoolers
- Performance exhaust systems
- Engine management system tuning
Challenges and Considerations
While turbocharged diesel engines offer numerous benefits, there are some challenges to consider:
- Complexity: Turbochargers add complexity to the engine system, potentially increasing maintenance requirements.
- Turbo Lag: There can be a slight delay in power delivery as the turbocharger spools up, known as turbo lag.
- Heat Management: Turbocharged engines generate more heat, requiring robust cooling systems.
- Cost: Initial costs for turbocharged engines and their components are typically higher than naturally aspirated alternatives.
The Future of Turbocharged Diesel Engines
As environmental regulations become stricter and the demand for fuel efficiency increases, turbocharged diesel engines continue to evolve. Some emerging trends include:
- Electric Turbochargers: These eliminate turbo lag and improve overall efficiency.
- Variable Geometry Turbochargers: Offer better performance across a wider range of engine speeds.
- Multi-Stage Turbocharging: Uses two or more turbochargers to optimize performance at different engine speeds.
- Hybrid Turbo-Electric Systems: Combine turbocharging with electric motors for improved efficiency and power delivery.
Environmental Impact and Emissions Control
Modern turbocharged diesel engines incorporate advanced emissions control technologies to minimize their environmental impact:
- Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR): Uses a urea-based solution to convert NOx emissions into harmless nitrogen and water.
- Diesel Particulate Filters (DPF): Trap and eliminate particulate matter from exhaust gases.
- Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR): Reduces NOx emissions by recirculating a portion of exhaust gases back into the combustion chamber.
- Advanced Fuel Injection Systems: Precise fuel delivery helps optimize combustion and reduce emissions.
Closing Thoughts
Turbocharged diesel engines have transformed the landscape of power generation in various industries. Their ability to deliver increased power, improved fuel efficiency, and reduced emissions makes them an attractive option for various applications. As technology advances, we can expect even more innovative solutions to enhance these remarkable powerplants’ performance and environmental friendliness.
By understanding the principles behind turbocharged diesel engines and staying informed about the latest developments, operators and enthusiasts can make the most of these powerful and efficient systems. Whether you’re managing a fleet of heavy-duty trucks or considering a diesel-powered vehicle for personal use, the benefits of turbocharged technology are clear and compelling.