RAID technology, or Redundant Array of Independent Disks, is foundational in today’s data storage solutions. By combining multiple disk drives into a single unit, RAID offers improved performance and redundancy. The primary goal is to protect data against drive failures while optimizing read and write speeds. Various RAID levels exist, each catering to different needs—whether it’s maximizing speed, ensuring data protection, or balancing both. The P411 supports multiple RAID configurations, allowing users to tailor their setups to meet specific operational requirements.
The Evolution of RAID
Since its inception, RAID has undergone significant advancements. Initially designed to bridge the gap between expensive mainframe disk systems and cost-effective personal computer storage, RAID continues to evolve. Modern RAID solutions offer sophisticated algorithms that ensure data reliability and accessibility, making them vital for businesses relying on big data analytics and high-speed transactions. The P411, with its versatility and support for various RAID levels, embodies this evolution by accommodating diverse storage needs with ease.
Why RAID Matters
In an era where data is king, ensuring its availability and integrity is paramount. RAID technology offers multiple benefits, including increased data protection, enhanced performance, and cost efficiency. By distributing data across multiple disks, RAID mitigates the risk of data loss due to disk failure. Additionally, RAID can improve read and write speeds by spreading operations across several disks, making it ideal for environments demanding high-speed data access. For these reasons, RAID has become a critical component in data center infrastructure, and the P411 stands out as a preferred choice for implementing these benefits.
Types of RAID Levels
Several RAID levels exist, each offering different balances of performance, redundancy, and cost. Common configurations include:
- RAID 0 (Striping): Offers increased performance but no redundancy.
- RAID 1 (Mirroring): Provides redundancy by duplicating data on two disks.
- RAID 5 (Striping with Parity): Balances performance and redundancy using parity data.
- RAID 6 (Dual Parity): Enhanced protection by using two parity blocks, allowing for multiple disk failures.
- RAID 10 (Mirroring and Striping): Combines RAID 1 and RAID 0 for both performance and redundancy.
The P411 supports many of these RAID levels, allowing administrators to create tailored solutions that best fit their operational needs.
Features and Specifications of the P411 Card
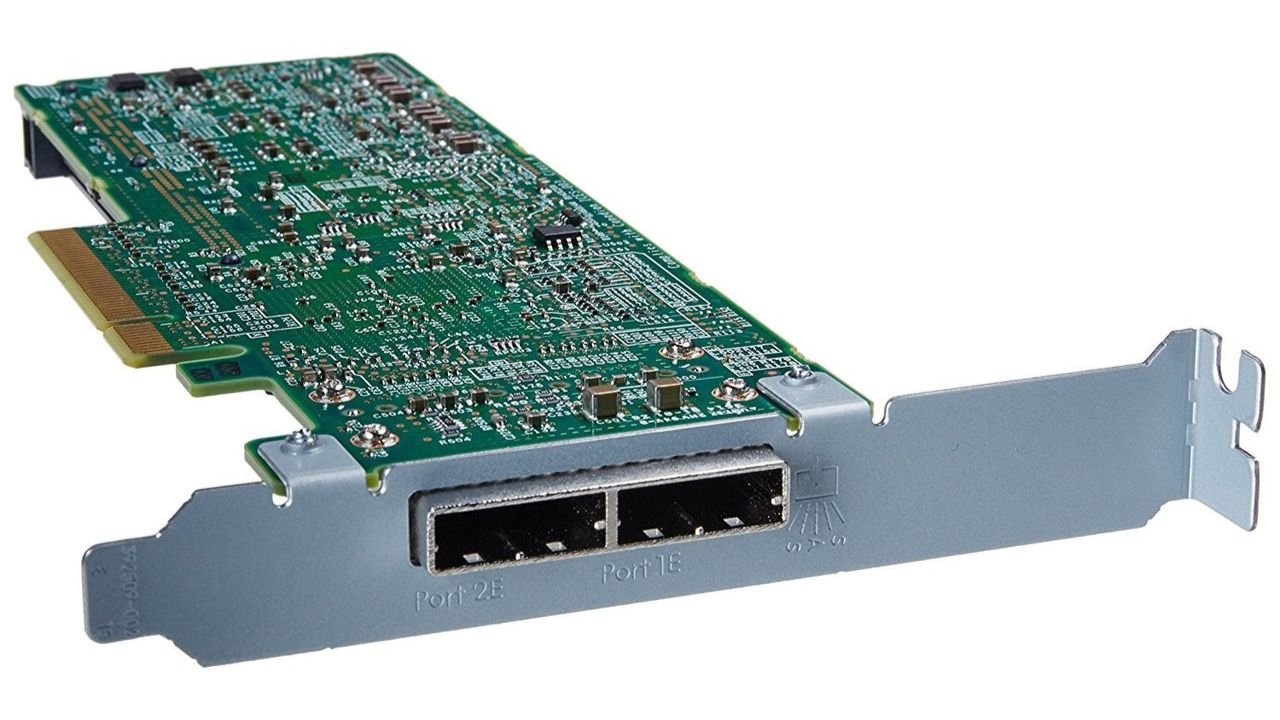
The HP Smart Array P411 RAID card is packed with features designed to optimize storage solutions. At its core, the P411 provides high-performance RAID functionality, supporting up to 8 SAS or SATA drives. With a 6 GB/s SAS interface, it ensures fast and reliable data transfers. The card also features a 512 MB battery-backed write cache, enhancing data protection during power outages.
Key Features
- High-Speed Data Transfer: The 6GB/s SAS interface allows rapid data movement, minimizing bottlenecks in data-intensive environments.
- Battery-Backed Write Cache: Protects data during unexpected power losses, ensuring all cached data is written to disk when power is restored.
- Flexible Drive Support: Compatible with both SAS and SATA drives, providing versatility in storage configurations.
- Advanced Data Protection: Supports several RAID levels, allowing for configurations that prioritize data integrity and speed.
Technical Specifications
Understanding the specifications can help you leverage the P411 to its fullest potential:
- Interface: PCI Express 2.0 x8
- Cache Memory: 512 MB, battery-backed
- Drive Support: Up to 8 SAS/SATA drives
- RAID Support: RAID 0, 1, 1+0, 5, 6
Compatibility and Integration
The P411 seamlessly integrates into existing systems, thanks to its broad compatibility with HP ProLiant servers. This integration ensures that businesses can upgrade their storage capabilities without overhauling their current infrastructure. The P411’s design supports hot-swapping, meaning drives can be replaced without shutting down the system, minimizing downtime and maintaining productivity.
Installation and Configuration Guide
Setting up the HP Smart Array P411 RAID card can be straightforward if you follow the right steps. This section will guide you through the installation and configuration process, helping ensure that your RAID card is operational and optimized for your storage needs.
Initial Setup
Begin by ensuring that your server is powered off and disconnected from any power source. Locate the appropriate PCIe slot on your server motherboard and carefully insert the P411 RAID card, ensuring it is securely seated. Once installed, connect the suitable cables from the card to the drives you wish to manage. After confirming all connections are secure, power on the server.
Configuring RAID Arrays
Upon booting, access the RAID setup utility by pressing the designated key during startup (usually F8 or F10). Within the utility, you’ll have the option to create and manage RAID arrays. Select the drives you wish to include in your array and choose the desired RAID level. Follow the prompts to complete the setup and save your configurations.
Finalizing the Installation
After configuring the RAID, ensure your operating system recognizes the newly created arrays. You may need to install additional drivers or software provided by HP to enhance functionality. Finally, test the setup by transferring files to and from the array, verifying speed and stability.
Performance Comparison with Other RAID Cards
The P411 RAID card excels in performance, but how does it stack up against competitors? Comparing its capabilities to other RAID cards can provide a clearer picture of its strengths and potential limitations.
Benchmarking the P411
The P411 RAID card consistently delivers high-speed data transfers, thanks to its 6GB/s SAS interface. In various benchmark tests, the card outperformed many of its peers, especially in scenarios requiring rapid data read and write capabilities. Its battery-backed cache plays a crucial role in maintaining performance stability even under load-intensive conditions.
Pros and Cons
While the P411 boasts impressive features, it’s essential to consider both its advantages and potential drawbacks:
- Pros:
- Fast data transfer rates
- Reliable data protection features
- Flexible RAID support
- Cons:
- May require additional drivers for optimal performance
- Limited to 8 drive support
Alternatives to Consider
While the P411 is an excellent choice, consider alternative RAID cards if your specific needs extend beyond its capabilities. Cards like the LSI MegaRAID and Adaptec series offer different features, such as higher drive support or integrated software functionality, which might better suit particular enterprise environments.
Use Cases and Application in Real-World Scenarios
The HP Smart Array P411 RAID card finds its place in various real-world applications, thanks to its versatility and reliability.
Data Centers
In data centers, where uptime and data integrity are of utmost importance, the P411 shines. Its ability to support multiple RAID levels ensures that data remains protected while providing the speed necessary for handling large volumes of information.
Enterprise Environments
For enterprises requiring robust storage solutions, the P411 offers a balance of performance and reliability. Whether used for database management, virtual machine hosting, or backup storage, the card’s features cater to diverse business needs.
Small to Medium Businesses
Small to medium-sized businesses can also benefit from the P411’s capabilities without the need for extensive infrastructure investments. Its compatibility with various server configurations makes it an accessible option for businesses looking to optimize their storage systems.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting Tips
Proper maintenance and troubleshooting are essential to ensure the continued performance of your P411 RAID card. This section offers practical tips to keep your system running smoothly.
Regular Maintenance
Perform regular checks of your RAID configuration and storage drives. Ensure that firmware is updated to the latest version, as updates often include performance enhancements and bug fixes. Cleaning the card and its connections can prevent dust buildup, which can lead to overheating.
Common Troubleshooting Steps
If issues arise, begin by checking all physical connections. Loose cables are a common culprit for RAID failures. Use diagnostic tools provided by HP to identify potential problems within the system. If a drive fails, replace it promptly, and allow the RAID array to rebuild.
When to Seek Professional Help
While many issues can be resolved with troubleshooting, some may require professional intervention. If problems persist or you notice unusual behavior in your RAID system, contact your vendor or a certified technician for assistance.
Future Trends in RAID Technology and the Role of P411
RAID technology continues to evolve, driven by the increasing demands for data storage and retrieval. Understanding future trends can help you prepare for upcoming changes and opportunities.
The Rise of Software-Defined Storage
Software-defined storage (SDS) is gaining traction, offering a flexible approach to managing storage resources. By decoupling storage software from hardware, SDS allows for more dynamic and scalable solutions. The P411 can serve as a foundation for organizations transitioning to SDS, providing a reliable hardware platform for initial implementations.
Integration with Cloud Systems
As more businesses migrate to the cloud, the integration of RAID technology with cloud storage becomes increasingly relevant. Hybrid solutions, combining on-premises RAID systems like the P411 with cloud storage, offer the benefits of both worlds—speed and redundancy with scalability and accessibility.
The Role of AI in RAID
Artificial intelligence is making its way into RAID management, with AI-driven algorithms optimizing array configurations and predictive maintenance tasks. While the P411 does not directly incorporate AI, its flexibility makes it well-suited for integration with next-generation technologies.
You May Also Like: Xcellon Dual USB 3.1 Card Reader/Reg Revolutionizes Data Management
Conclusion
The HP Smart Array P411 RAID card offers a comprehensive solution for businesses looking to optimize their storage capabilities. From its robust feature set to its adaptability across various environments, the P411 remains a popular choice among IT professionals and server administrators. By understanding its capabilities and applications, you can leverage the P411 to enhance data protection, performance, and overall system reliability. Whether you’re managing a large data center or a small business IT infrastructure, the P411 provides the tools necessary to meet your storage needs effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main purpose of the P411 RAID card?
The HP Smart Array P411 RAID card is designed to manage multiple hard drives as a single unit, providing redundancy and improved storage performance for various applications.
Can the P411 support both SAS and SATA drives?
Yes, the P411 RAID card is compatible with both SAS and SATA drives, offering flexibility in configuring storage solutions based on specific needs.
How does the battery-backed write cache benefit the P411?
The battery-backed write cache protects data during power outages by ensuring that all cached data is written to disk when power is restored, enhancing data integrity.
Is the P411 compatible with non-HP servers?
While the P411 is primarily designed for HP ProLiant servers, it can be integrated into non-HP systems, provided they have a compatible PCIe slot for installation.
What RAID levels does the P411 support?
The P411 supports multiple RAID levels, including RAID 0, 1, 1+0, 5, and 6, allowing for customizable configurations that balance performance and redundancy.