Introduction to Fiberglass-Reinforced HDPE
The evolution of construction materials continues to drive innovation in building stronger, safer, and longer-lasting structures. At the forefront of these advancements is fiberglass-reinforced high-density polyethylene (HDPE). By merging the natural flexibility of HDPE with the added strength and rigidity of fiberglass, this composite is becoming a preferred choice where reliable load-bearing capacity is essential. Industries that rely on heavy-duty supports often benefit from advanced products like composite cribbing blocks, which exemplify the versatility and strength of fiberglass-reinforced HDPE in real-world applications.
These improvements are not just limited to construction. Industrial facilities, event organizers, and emergency response teams are leveraging the superior load distribution and stability offered by fiberglass-reinforced HDPE. The adoption of this composite aligns with industry trends that prioritize materials that provide high strength, environmental resilience, and ease of use.
Understanding the Composition and Properties
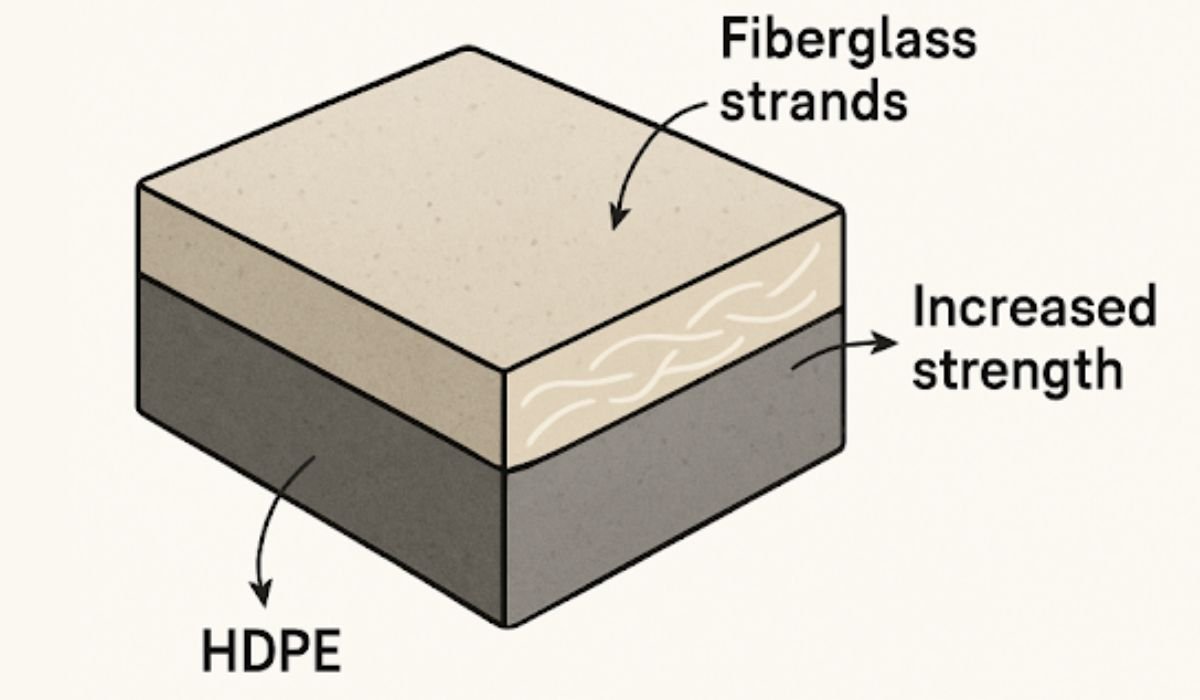
Fiberglass-reinforced HDPE is designed to deliver the best of both core materials. Conventional HDPE is widely respected for its chemical resistance, lightweight nature, and flexibility. However, on its own, HDPE has limitations in terms of strength and its ability to handle heavy or uneven loads. By integrating fiberglass into the polymer matrix, the composite offers improved tensile strength, longevity, and enhanced shape retention under pressure.
The fiberglass strands within the HDPE matrix act as a skeletal support, distributing stress more evenly and resisting deformation under heavy loads or cyclical loads. This property makes fiberglass-reinforced HDPE ideal for use in environments where traditional materials like concrete, wood, or plain HDPE may crack, corrode, or deform under constant use.
Applications in Infrastructure
The practical advantages of fiberglass-reinforced HDPE are evident in infrastructure projects for roads, bridges, culverts, and more. For example, in concrete reinforcement, the installation of HDPE liners reinforced with fiberglass has been shown to increase the structure’s load-bearing capacity significantly. Documented research indicates that these composite-reinforced liners can enhance ultimate load capacity by up to 67 percent and increase initial stiffness by up to 3.6 times compared to traditional designs.
Beyond civil infrastructure, the material is increasingly used in custom foundation pads, retaining wall systems, and lifting blocks. These uses benefit from the combination of flexibility and strength that is difficult to achieve with either fiberglass or HDPE alone. Fiberglass-reinforced HDPE is also highly valued in sectors that require rapid deployment of stable platforms, such as shipping, energy, and disaster recovery.
Advantages Over Traditional Materials
- Corrosion Resistance: Unlike steel and most metal-based alternatives, fiberglass-reinforced HDPE is not susceptible to rust or chemical reactions, making it suitable for challenging environments exposed to moisture and industrial chemicals.
- Lightweight Construction: Reducing the weight of individual components makes transportation, installation, and post-installation adjustments more manageable, thereby significantly reducing construction time and labor costs.
- Flexibility for Complex Designs: Unlike rigid materials, fiberglass-reinforced HDPE can be formed into a broad range of geometries without sacrificing its structural performance. This flexibility supports innovative engineering designs for specialized infrastructure needs.
The combined benefits frequently tip the cost-to-value ratio in favor of fiberglass-reinforced HDPE, especially for projects where long-term durability, resistance to harsh environmental factors, and simplified on-site handling are strategic advantages. For a detailed comparison of material properties and costs, major engineering publications such as ASCE Journals provide in-depth research and case studies.
Environmental Considerations
Environmental responsibility is an increasing priority in engineering, and fiberglass-reinforced HDPE aligns with sustainability goals by accommodating recycled content. When recycled HDPE fibers are used within composites, they can boost the mechanical properties and durability of building products. This dual benefit reduces plastic waste while enhancing the resilience of construction materials. These eco-friendly composites help minimize the carbon footprint of new developments and align with broader circular-economy initiatives in the construction industry.
Challenges and Considerations
- Initial Material Costs: The upfront investment for fiberglass-reinforced HDPE may exceed that of traditional materials, such as unreinforced plastics or certain metals. Manufacturers and project managers often find that these costs are recouped by significantly reduced maintenance and longer material lifespan.
- Complex Manufacturing: Producing high-quality fiberglass-reinforced HDPE requires advanced processing technology and skilled manufacturers. This challenge is being addressed as more producers incorporate composite manufacturing expertise, but it remains a consideration during project planning and procurement.
Future Prospects
With ongoing research and development, the range of potential uses for fiberglass-reinforced HDPE continues to expand. Increasingly sophisticated formulations and manufacturing techniques are unlocking even greater performance characteristics suited to sectors such as marine facilities, automotive parts, railway infrastructure, and renewable energy. As more industries explore the synergistic benefits of composites, fiberglass-reinforced HDPE is likely to become a staple material in the next generation of load-bearing applications.
Trends in global construction and infrastructure further suggest an uptick in demand for solutions that minimize maintenance while maximizing safety and environmental stewardship. Continued investment in developing new resin and fiber blends will likely yield products tailored to even more demanding environments and performance standards.
Conclusion
Fiberglass-reinforced HDPE represents a significant leap forward for materials engineering in the load-bearing sector. Its ability to combine strength with durability, corrosion resistance with lightweight construction, and sustainability with adaptability makes it a wise choice for a wide variety of modern challenges. As industries continue to seek materials that meet high-performance and green standards, fiberglass-reinforced HDPE is expected to play an increasingly vital role in the future of construction, infrastructure, and industrial safety.
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE: Durable Fiberglass Panels for Building Efficiency